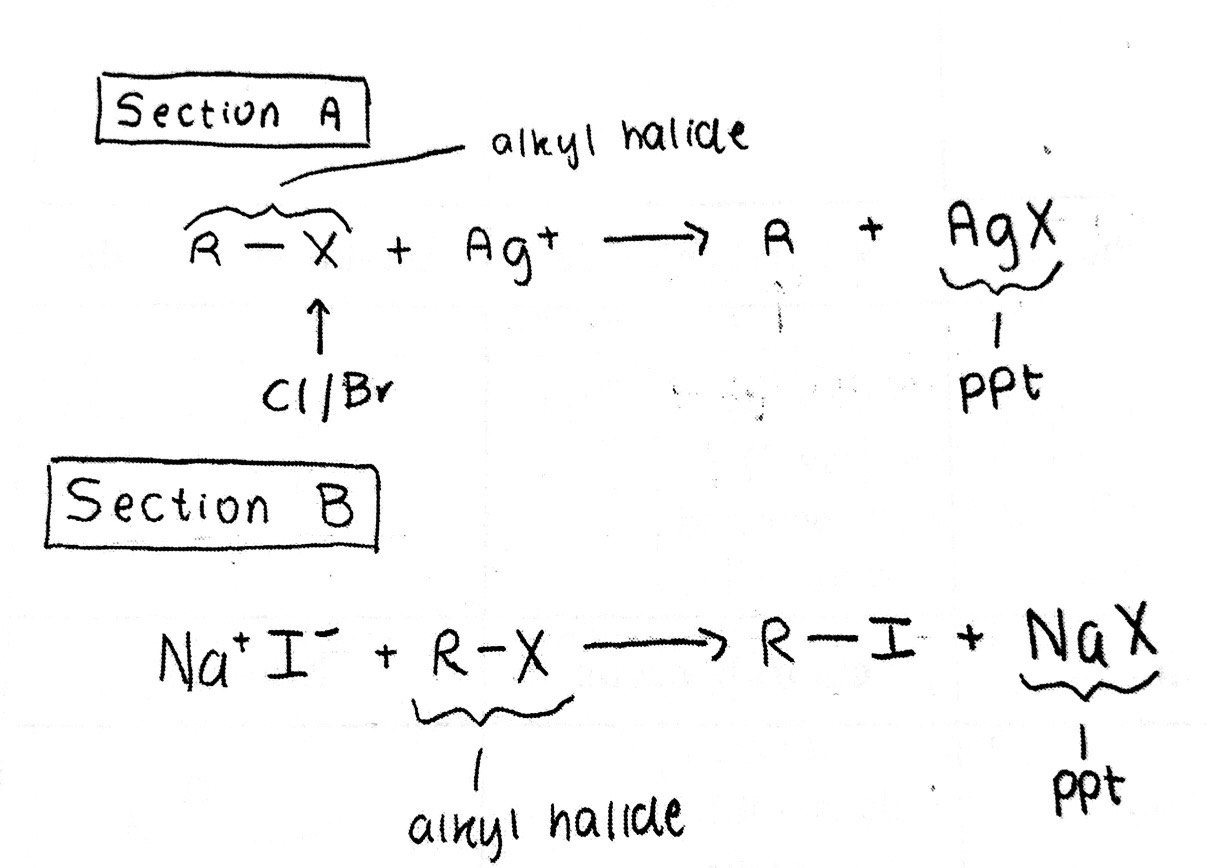
Reaction of Alkyl Halides With Silver Nitrate
S N 2 conditions. Silver nitrate AgNO 3 in ethanol.

What Is The Mechanism Of The Reaction Of Alkyl Halide With Silver Nitrite Quora
Acetone is a good solvent for Sn2 reactions because it is a polar aprotic solvent.
. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. We will be examining Sn2 reactions with an ethanolic solution of silver nitrate. The equation for the reactions are CH3-CH2-CH2-CH-Cl AgNO3.
On treating ethanolic solution of haloalkane with silver nitrite A g O N O nitroalkane is formed because since the bond between A g O is covalent the lone pair on nitrogen acts as an attacking site for nucleophilic substitution. As shown in the diagram above a highly polar solvent ethanol is used to dissolve the butyl chloride. The overall reaction is shown in equation 1.
Nothing else is added. Reactivity of alkyl halides towards this reagent is. This is because the t-butyl chloride containing tertiary alkyl group which reacts rapidly via SIN mechanism with the silver nitrate to form a precipitate of silver chloride.
The reaction by looking for the first appearance of the solid salts. In this experiment you will explore the reactivity of several alkyl. Consequently in the present study reaction is initiated at ice temperature and then completed at room temperature.
Then silver nitrate solution is added. The second section of the experiment compared the reaction rates of the same four alkyl halides as they were mixed with a solution containing silver nitrate in ethanol. The rate at which the silver halide salt precipitate forms is characteristic of different.
When an alkyl halide is exposed to an ethanolic solution of silver nitrate the silver ion coordinates with an electron pair on the halogen weakening the carbon-halogen bond and producing an insoluble silver halide. The reactions performed were SN2. A solution of sodium iodide NaI in acetone and a solution of.
For the reactions of the alkyl halides with 1 ethanolic silver nitrate did the type of balide affect the rate of the reaction Hint use your data chant to compare all structures which only vary by the type of halide Example. In the presence of ethanolic silver nitrate alkyl halides that can form stable carbocations react through an SN 1 mechanism to provide a substitution product in this case an ether derived from the alkyl halide and the ethanol nucleophile. Reaction of halides with ethanolic silver nitrate AgNO3EtOH Which alkyl halides did not react with ethanolic.
The mixture is acidified by adding dilute nitric acid. This prevents unreacted hydroxide ions reacting with the silver ions to give a confusing precipitate. The free electrophile will capture the first nucleophile it can find.
C4H9NO3AgCl CH3-CH2-CH2-CH-Br AgNO3. The nitrate ion is a weak nucleophile and ethanol promotes halide ionization. After addition of silver nitrate solution a white precipitate is formed with the one of bromine almost immediately.
Ethanol is a polar protic solvent that favors ionization of the alkyl halide to form stable carbocations. Furthermore because the re- action is exothermic diethyl ether is used as a dilu- ent. Pg645 In the former it gives precipitates with halides except the fluoride cyanides thiocyanates chromatesVI phosphateV and most ions of organic acids.
To each tube add 1ml of a 1 ethanolic silver nitrate solution mix the contents thoroughly. R 3 CX R 2 CHX RCH 2 X Procedure Add one drop or a couple of crystals of the unknown to 2 mL of 2 ethanolic silver nitrate solution. I chlorobutane VS 1-bromobutane and 2-chlorobutane VS 2.
Explain how this mechanism accounts for the relative rate of reactivity for 1 degree. Each compound will be treated with a solution of silver nitrate in ethanol. Alkyl halide by reaction with a hydrohalic acid.
Two nucleophilic reagents will be. The silver of the silver nitrate reagent acts as a Lewis acid to promote formation of the carbocation. 100 2 ratings Benzyl allyl and tertiary halides react immediately with silver nitrate.
This is facilitated by the silver ion coordinating to the halide through a lone pair on the halogen atom causing a weakening of the carbon-halogen bond. 339 for halide structures 2. This reaction is carried out by an SN1 mechanism.
Adding silver nitrate to a solution containing halide ions forms a silver halide. If no immediate reaction is observed stand for 5 minutes at. The silver ion coordinates with a lone pair on the halogen which begins to weaken the carbon-halogen bond.
The precipitate is due to reaction between the halide ions and silver ions. This includes tertiary alkyl carbocations E 7 8. When silver halides dissolve in ammonia solution they then form c omplex ions.
The reaction of silver nitrite with alkyl halides ought to be conducted at as low a temperature as possible. View the full answer. Part 2 Ethanolic Silver Nitrate Solution SN1 reaction 1.
After varying lengths of time precipitates appear as halide ions produced from reactions of the halogenoalkanes react with the silver ions present. When silver nitrate a soluble solution is mixed with a carbonate solution a precipitation reaction double replacement reaction takes place forming nitrate ions and the insoluble solid silver. For electrophiles with a parameter E 0 the reactions are essentially diffusion controlled ie.
Take 11 labeled tubes and add 01 ml or 01 g of the 11 halides see p. In this case various halogenoalkanes are treated with a solution of silver nitrate in a mixture of ethanol and water. The silver nitrate test is sensitive enough to detect fairly small concentrations of halide ions.
The chloride will unionize to the butyl caution and chloride ion. Not parallel to the results expected. The Silver Nitrate Test allows for the identification of alkyl halides by observing them in an alcoholic silver nitrate environment.
Alkyl halides that undergo the S l substitution reaction react with alcoholic silver nitrate AgNOs to form a precipitate of the corresponding silver halide. Halides and one aryl halide under both S N 1 and. Write a mechanism for the reaction of an alkyl halide with alcoholic silver nitrate which demonstrates the type of substituition which occurs.
Twine created by Dr. Samantha Reynolds UNH Manchester. Note the time of first appearance of any precipitate AgCl or AgBr in each test tube.
Silver is a transition metal and ammonia is an example of a ligand - a species with a lone pair of electrons that can bond to transition metals with a dative covalent bond also called a coordinate bond. R O N O R X N O X 2 X R N O X 2.

How Do You Predict The Reactivity Of Alkyl Halides In Chegg Com

Silver Catalyzed Benzylation And Allylation Reactions Of Tertiary And Secondary Alkyl Halides With Grignard Reagents
No comments for "Reaction of Alkyl Halides With Silver Nitrate"
Post a Comment